FreePBX 12 with CLEARMODE support
Before i start i have to explain what clearmode is and when you need it.
CLEARMODE
A phone call is 64Kbps (PCM sampled audio with 8 bit depth * 8000 hz sample rate per direction). A basic rate ISDN connection contain 2 of these channels plus a small channel for signaling. You use the same 64 Kbps PCM codec on SIP calls and it is then called μLaw or aLaw depending on region.
ISDN also supports data calls. A modem will then get a full duplex 64Kbit connection to the other modem. ISDN have two channels so you can bundle your two 64Kbps connections and get 128Kbps. This was very cool, and expensive, in the 90s!
If you have the equipment to connect ISDN to SIP you will soon discover that you can only make voice calls. Data connections will fail.
The solution is clearmode. Clearmode is a "transparent codec" that takes the 64Kbps data stream and changes nothing with it. The PBX sends the 64Kbps data stream like a regular voice call. On the other side of the connection it have to be connected somehow to another modem. More information about the codec can be found here (RFC 4040).
This codec is is used by the few (mostly germans) who still have ISDN equipment and want it to connect over SIP instead of the old phone system.
Asterisk, Freeswitch and YATE don't have the codec by default but there are patches for all three. In this guide i will use FreePBX that is based on Asterisk.
But wait! You are not german? Swedes can be interested in ISDN too :)
Guide
This guide assumes you use FreePBX 17 on Debian 12. It will work if the call both enters and leaves the PBX as SIP. It doesn't work if the call enters or leaves the PBX through DAHDI.
If your system isn't up to date start by updating your system
apt update && apt upgradeThen install asterisk22-devel to get some asterisk headers.
apt install asterisk22-develNow you need the source code for the codec module. You can get it on github
copy and run the two gcc lines in the file header.
gcc -pipe -Wall -Wstrict-prototypes -Wmissing-prototypes -Wmissing-declarations -g3 -Iinclude -I../include -D_REENTRANT -D_GNU_SOURCE -O6 -fomit-frame-pointer -Wno-missing-prototypes -Wno-missing-declarations -DCRYPTO -fPIC -c -o codec_clearmode.o codec_clearmode.c
gcc -shared -Xlinker -x -o codec_clearmode.so codec_clearmode.o
That will compile the codec module.
Next step is to install the codec by copying in to /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/asterisk/modules/
cp codec_clearmode.so /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/asterisk/modules/
Open the asterisk CLI and load the module to verify that it loads without issues.
retronet-freepbx17*CLI> module load codec_clearmode.so
Loaded codec_clearmode.so
retronet-freepbx17*CLI>It loaded without issues. Great!
Unless you exclude the module it will load automatically but it in some cases it loads after SIP connections are made. Therefore we need to preload the module.
The built in Asterisk Modules configuration is buggy in my freepbx installation. Therefore we have to edit /etc/modules.conf
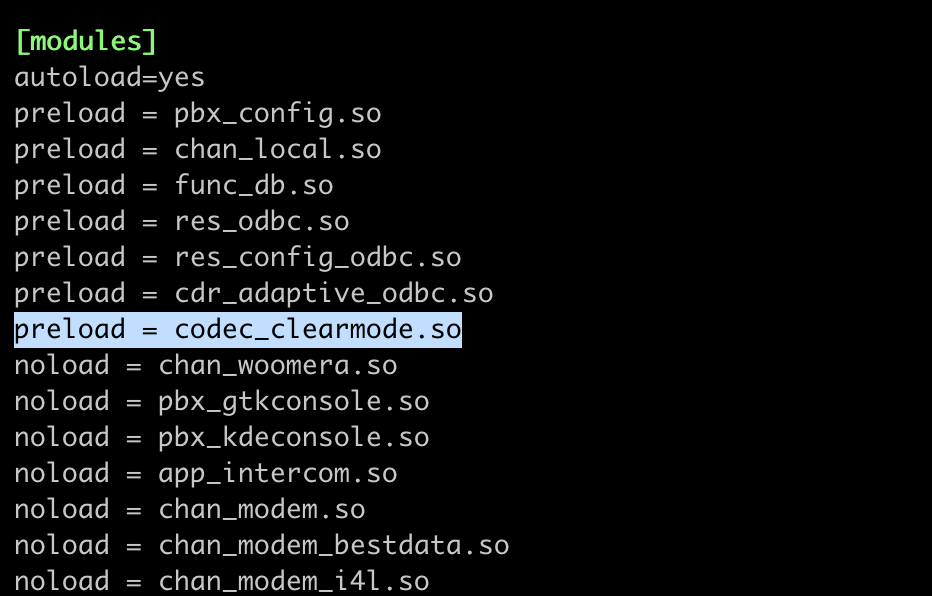
Open /etc/modules.conf in your favorite text editor and add preload = codec_clearmode.so like this:
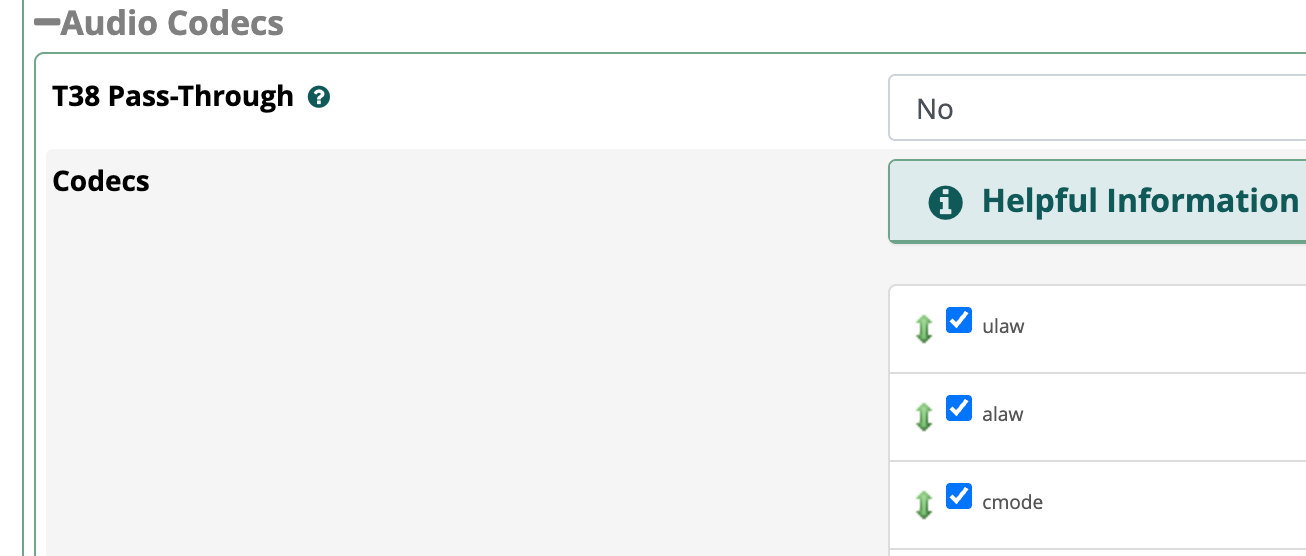
Next we want to allow the use of the codec in calls. Open the FreePBX web interface and navigate to Settings -> Asterisk SIP Settings.
Scroll down to Codecs. Check the box next to cmode and click submit.
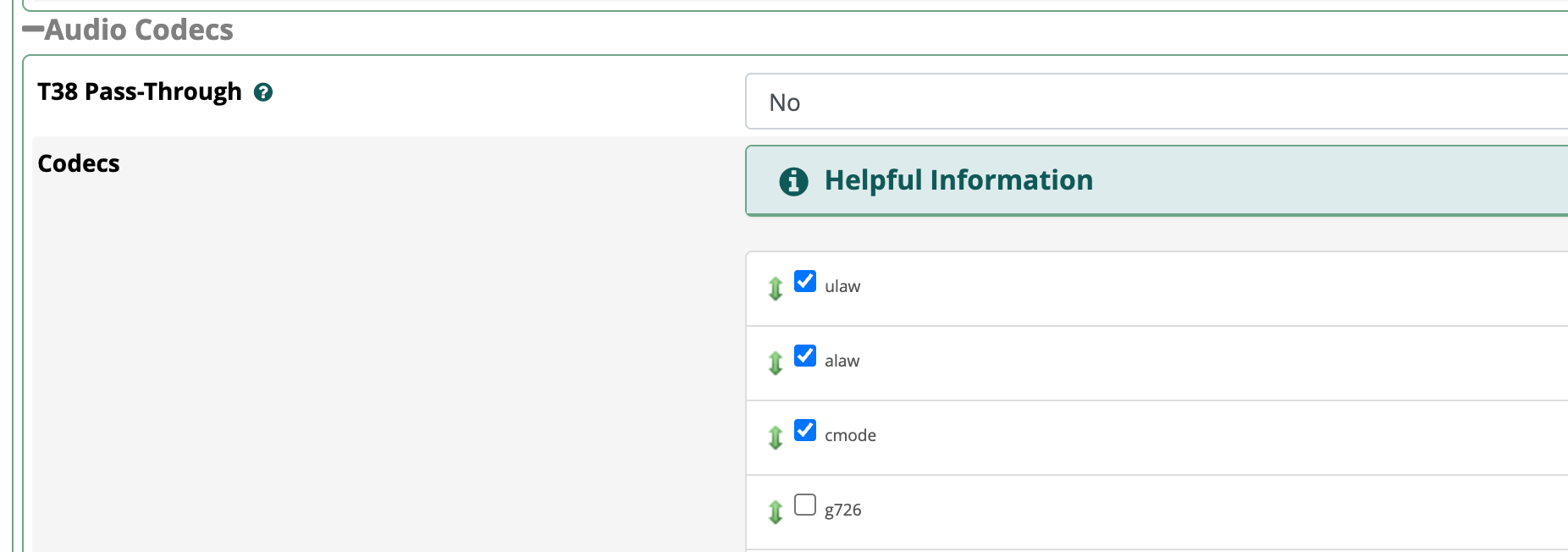
The same thing have to be done on your trunks that you want to send clearmode calls to.
Now you should be able to make clearmode calls between extensions and trunks!
